The shift from a fee-for-service healthcare delivery model to a value-based care model, has significantly changed the way healthcare is delivered and reimbursed in the United States.
What Is Value-Based Healthcare?
Value-based healthcare is a healthcare delivery framework that incentivizes healthcare providers to focus on the quality of services rendered, as opposed to the quantity. Under a value-based healthcare model, healthcare providers (including hospitals and physicians) are compensated based upon patient health outcomes.
How Does Value-Based Healthcare Work?
Prices are quantified and established based on the performance of the physicians and the historical prices of the services rendered. This puts much more emphasis on ensuring that providers take care of patients’ needs to the best of their ability in as few visits as possible rather than simply treating symptoms and waiting for patients to return.
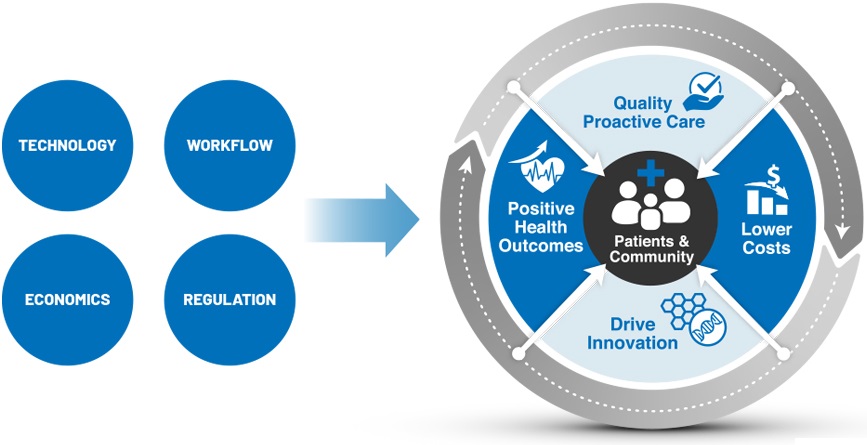
Benefits of Value-Based Care Models
Since healthcare costs are rising and patient satisfaction is often not, it has become vital to healthcare providers and payers that new techniques for billing and revenue cycle management be adopted.
Higher Efficiency of Care & Greater Patient Satisfaction
Since VBC models are reliant on quality, providers focus on providing medical solutions that work over the long term and on developing relationships with patients.
Patients Spend Less Money But Have Better Health
Because VBC is not dependent on the number of services provided, but rather their quality, patients won’t have to pay for things they didn’t need or that wouldn’t have worked. The focus is on providing personalized solutions that are agreed upon between them and their provider and which will lead to better outcomes in the long run. VBC rewards these outcomes for both the patient and the provider.
Prices Will Begin to Reflect Value
Physician services are often priced according to supply and demand principles, meaning prices are higher than many would desire or can afford. However, using Value-Based Care models could contribute to price changes that reflect the value that medicines and services have for patients.
Healthier Society and Reduced Risk
Since one of the main goals of VBC is to help society and communities as a whole become healthier, financial risk is reduced because it is spread out more evenly. Because financial rewards are tied to the satisfaction of patients, the more patients are satisfied with their care, the more financially stable healthcare organizations and providers will be.
Reimbursement for Value-Based Care
When transitioning from FFS to value-based care, a variety of reimbursement approaches are available to healthcare providers. CMS has created several different reimbursement models, while commercial payers have followed with variations and models of their own (1).
How to Implement Value-Based Healthcare
If you are a healthcare professional, there are steps you can take to begin implementing value-based care in your practice. According to the American Medical Association (AMA), there are five steps healthcare providers can take to prepare their practices for value-based care:
- Identify your patient population and opportunity;
- Design the care model;
- Partner for success;
- Drive appropriate utilization, and;
- Quantify impact and continuously improve.
Summary
VBC models are becoming increasingly popular in government circles, especially where Medicaid and Medicare are concerned. With the heavy influence of these programs in mind, it’s likely that more providers will come to see the benefits of using VBC models to improve their revenue cycle management.
It will be important in the continuing future for healthcare organizations to look more closely at their revenue models and determine where costs can be cut while still maintaining patient satisfaction.




